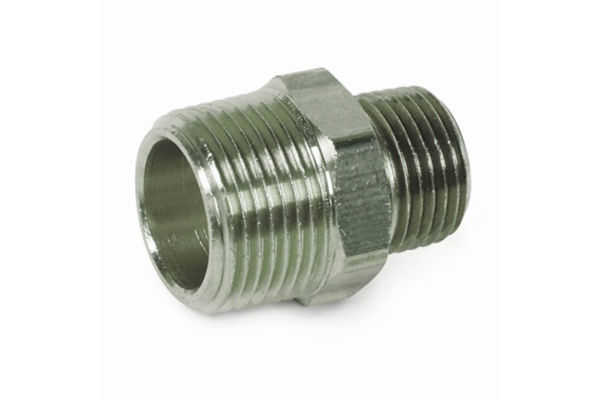
The forging process of Forged Fitting generally includes the following steps:
Raw material preparation: Select suitable metal materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, etc. based on the performance requirements of the forged pipe fittings, usually purchased in the form of bars, steel ingots, etc. Inspect the raw materials to ensure that their chemical composition, mechanical properties, etc. meet the standard requirements, and perform surface cleaning to remove impurities such as oxide scale and oil stains.
Heating billet: Place the prepared billet into a heating furnace and heat it. The heating temperature varies depending on the material, usually around 1000 ℃ -1200 ℃, to achieve the appropriate forging temperature range for the metal billet, improve its plasticity, and reduce deformation resistance.
Forging operation: Equipment such as air hammers and friction presses are used to apply pressure or impact force to the heated billet, causing it to undergo plastic deformation. For pipes with simple shapes, they can be directly forged one or more times to achieve a rough shape; For pipes with complex shapes, it may be necessary to use a multi-step forging process to gradually complete the forming of the pipe.
Control forging ratio: Forging ratio is an indicator to measure the degree of metal deformation during the forging process. Generally, the forging ratio is between 3-5, and the internal structure and mechanical properties of the pipe fittings are ensured by controlling the forging ratio.
Cooling and heat treatment: After forging, suitable cooling methods such as air cooling, water cooling, oil cooling, etc. are selected based on material and performance requirements. After cooling, in order to improve the structure and performance of the pipe fittings, heat treatment such as normalizing, tempering, quenching, etc. is usually required.
Subsequent processing and inspection: Mechanical processing such as turning, milling, drilling, etc. is performed on the forged pipe fittings to meet the requirements of dimensional accuracy and surface quality. Comprehensive inspection of pipe fittings is carried out through visual inspection, dimensional measurement, non-destructive testing, and other methods to ensure that product quality meets standards and customer requirements.
 Language
Language Espanol
Espanol English
English Italian
Italian عربى
عربى
 Skype: chinamaker99
Skype: chinamaker99  Tel: 86-316-5120812
Tel: 86-316-5120812 Email:
Email:  Whatsapp:
Whatsapp: